04 Oct What is Foreign Trade?
The Meaning and Definition of Foreign Trade or International Trade!
Foreign trade or international trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories. It is the trading of goods and services that are destined for a country other than their country of origin. Foreign trade can also be investing in foreign securities, though this is a less common use of the term.
In most countries, Foreign trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product (GDP). While international trade has been present throughout much of history, its economic, social, and political importance has been on the rise in recent centuries.
While international trade has existed throughout history (for example Uttarapatha, Silk Road, Amber Road, scramble for Africa, Atlantic slave trade, salt roads), its economic, social, and political importance has been on the rise in recent centuries.
Carrying out trade at an international level is a complex process when compared to domestic trade. When trade takes place between two or more nations factors like currency, government policies, economy, judicial system, laws, and markets influence trade.
To smoothen and justify the process of trade between countries of different economic standing, some international economic organisations were formed, such as the World Trade Organization. These organisations work towards the facilitation and growth of international trade. Statistical services of intergovernmental and supranational organisations and national statistical agencies publish official statistics on international trade.

Foreign trade is all about imports and exports. The backbone of any trade between nations is those products and services which are being traded to some other location outside a particular country’s borders. Some nations are adept at producing certain products at a cost-effective price. Perhaps it is because they have the labor supply or abundant natural resources which make up the raw materials needed. No matter what the reason, the ability of some nations to produce what other nations want is what makes international trade work.
All countries need goods and services to satisfy wants of their people. Production of goods and services requires resources. Every country has only limited resources. No country can produce all the goods and services that it requires. It has to buy from other countries what it cannot produce or can produce less than its requirements. Similarly, it sells to other countries the goods which it has in surplus quantities. India too, buys from and sells to other countries various types of goods and services.
Generally no country is self-sufficient. It has to depend upon other countries for importing the goods which are either non-available with it or are available in insufficient quantities. Similarly, it can export goods, which are in excess quantity with it and are in high demand outside.
International trade means trade between the two or more countries. International trade involves different currencies of different countries and is regulated by laws, rules and regulations of the concerned countries. Thus, International trade is more complex.
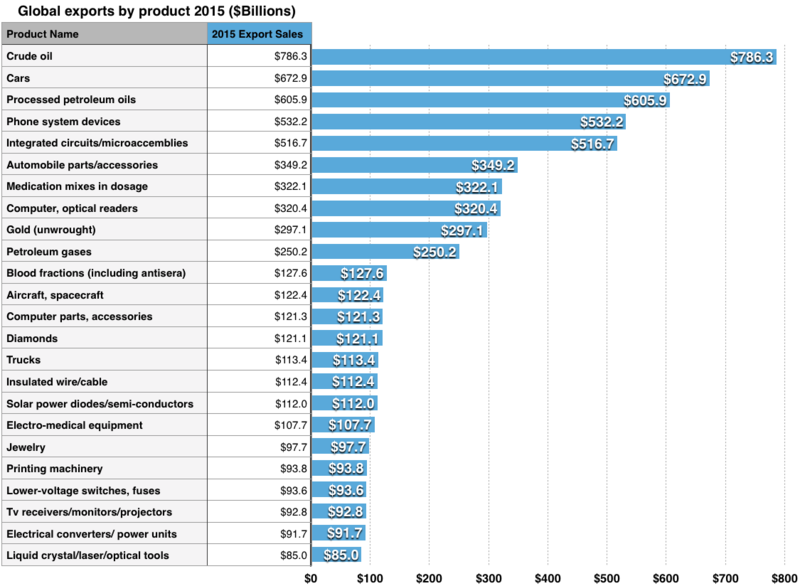
Most traded export products
According to Wasserman and Haltman, “International trade consists of transaction between residents of different countries”.
According to Anatol Marad, “International trade is a trade between nations”.
According to Eugeworth, “International trade means trade between nations”.
Click Here To Get A Letter Of Credit For Your Foreign Trade & Import / Export Transactions
Industrialization, advanced transportation, globalization, multinational corporations, and outsourcing are all having a major impact on the international trade system. Increasing international trade is crucial to the continuance of globalization. Without international trade, nations would be limited to the goods and services produced within their own borders.
International trade is in principle not different from domestic trade as the motivation and the behaviour of parties involved in a trade do not change fundamentally regardless of whether trade is across a border or not. The main difference is that international trade is typically more costly than domestic trade.
The reason is that a border typically imposes additional costs such as tariffs, time costs due to border delays and costs associated with country differences such as language, the legal system or culture. International trade consists of ‘export trade’ and ‘import trade’. Export involves sale of goods and services to other countries. Import consists of purchases from other countries.
International or Foreign trade is recognized as the most significant determinants of economic development of a country, all over the world. The foreign trade of a country consists of inward (import) and outward (export) movement of goods and services, which results into. outflow and inflow of foreign exchange. Thus it is also called EXIM Trade.
For providing, regulating and creating necessary environment for its orderly growth, several Acts have been put in place. The foreign trade of India is governed by the Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act, 1992 and the rules and orders issued there under. Payments for import and export transactions are governed by Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999. Customs Act, 1962 governs the physical movement of goods and services through various modes of transportation.
In some cases, the products produced in a foreign trade situation are very similar to other products being produced around the world, at least in their raw form. Therefore, these products, known as commodities, are often pooled together in one mass market and sold. This is called trading commodities. The most common commodities often sold in foreign trade are oil and grain.
There are a number of issues with imports and exports that must be taken into consideration when conducting foreign trade. For example, some countries have industries they may want to protect. These industries may be in competition with foreign companies for the opportunity to sell products domestically. To protect domestic trade, countries may institute tariffs, which are taxes on certain foreign goods. While this is a way to generate revenue, its real value lies in helping those domestic companies.
For example, to encourage domestic production of ethanol in the United States, a tariff has been imposed on Brazilian ethanol. This protects the ethanol market in the United States, which would not otherwise be able to compete with Brazilian ethanol based on cost. In Brazil, ethanol is made from sugar, which produces far more ethanol gallons per acre than corn, the primary crop used for ethanol in the United States.
In addition to tariffs, currency issues are another factor in foreign trade. Some companies selling products overseas prefer to be paid in a certain type of currency, such as the US Dollar or Euro. This protects the company in case the country involved in a trade experiences a rapid devaluation in currency. Most foreign trading agreements will always involve a relatively stable currency.





What is International Trade - Grand City Investment Ltd
Posted at 04:34h, 06 August[…] known as foreign trade, international trade has been maintained since the dawn of time. Trading goods were transported on […]